Federal Proximity Factor Tool: Out of Basin Compensatory Mitigation for U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE)
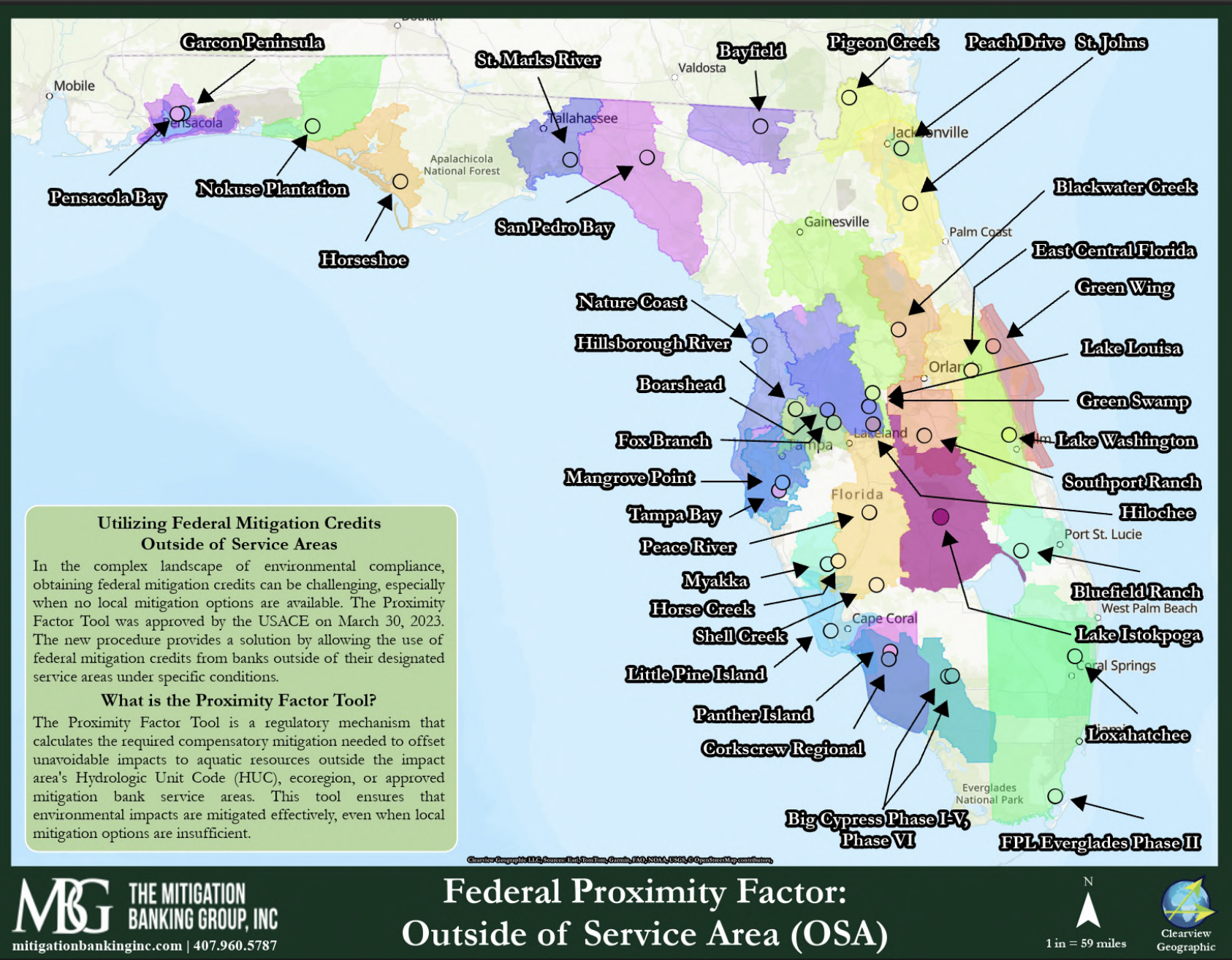
The Proximity Factor Tool plays a crucial role in determining the compensatory mitigation required when federal mitigation credits are used outside their designated service area. This tool, exclusively applicable to federal credits, ensures that mitigation remains effective even when no local mitigation options are available. It is regulated by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) and follows a case-by-case approval process, providing a structured framework for projects needing to offset environmental impacts in areas where no local federal credits exist.